HISTORY OF THE INSTITUTE
Institute of Engineering Thermophysics of NAS of Ukraine was created as a result of series reorganizations of energy scientific institutions that existed before in the system of the Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR.
In different years, the Institute’s scientific staff was headed by famous scientists:
 |
 |
 |
|
SHVETS |
SHCHEGOLEV German Mikhailovich Professor, Doctor of Engineering 1955 – 1964 |
TOLUBINSKYY |
 |
 |
 |
| BABUKHA Grigory Lukich Professor, Doctor of Engineering 1972 – 1973 |
HERASHCHENKO Oleg Arkadevich Corr. Member of Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR 1973 – 1982 |
DOLINSKY Anatoly Andreyevich Academician of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine Honorary Head of the Institute 1982 – 2015 |
 |
||
| SNEZHKIN Yuri Fedorovich Academician of National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine Since December 2015, the Head of the Institute |
INSTITUTE OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS OF NAS OF UKRAINE
Institute of Engineering Thermophysics of NAS of Ukraine was created as a result of series reorganizations of energy scientific institutions that existed before in the system of the Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR.
The development of research in the field of energy in the Academy of Sciences was initiated in 1939, when was organized the Institute of Energy of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR in Kharkiv and its affiliates in Kyiv. The main tasks of the Institute and affiliate were the scientific substantiation of the electrification’s development of the republic on the basis of the complex using energy resources, development of methods for increasing the efficiency of energy equipment.

Ivan Trokhymovich Shvets (1901 – 1983)
Academician of the Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR, Doctor of Engineering, Professor
Honored Worker of Science and Technology of the UkrSSR, Head of Institutes
power engineering (1941-1947) and heat power engineering of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR (1947 – 1955),
Rector of Kyiv State University by named T. G. Shevchenko (1955 – 1972),
chief academic secretary of the Presidium of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR (1950 – 1952),
Academician-Secretary of the Presidium of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR (1970 – 1978),
Deputy Chairman of the Verkhovna Rada of the UkrSSR (1967 – 1970)
Institute consisted of four departments, these were: electrical engineering, heat engineering, hydrotechnical and dynamics of power machines. They headed by academician of the Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR V.M. Khrushchev, academician of the Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR G.F. Proskura (the second and third departments) and Corresponding Member of Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR V.I. Mayzel. In the Kyiv’s branch there was a group of general energy problems and a laboratory for heat exchange and heat modeling (heads were I.T. Shvets and V.I. Tolubinsky; later they became academicians of the Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR).
Before the beginning of the Great Patriotic War in the Institute new methods for calculating hydromachines and principles for the creation of closed-loop gas turbine plants were developed.
In May 1947 the Institute was divided into the Institute of Heat Power Engineering and the Institute of Electrical Engineering of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR. The Institute of Heat Power Engineering of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR was headed by I.T. Shvets (1947-1952 and 1954-1955), V.I. Tolubinsky (1953-1954 and 1964), G.M. Shchogolev (1955 – 1963).
First, the Institute of Heat and Power Engineering of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR was carrying out the research on the improvement of heat engines, the intensification of heat transfer processes in various technical devices and on general problems of the development of the energy sector of the republic. In the structure of the Institute were four laboratories – theoretical heat engineering, gas turbines, heat engines and sets, fuel using and industrial heat engineering and the department of general energy. They were led respectively by professors I.I. Chornobylsky, P.D. Shvetsov, I.T. Shvets, V.I. Tolubinsky and F.T. Markovsky. Later, in 1949, the Institute was entrusted with the development of scientific bases and practical methods of energy technology using of Ukrain’s brown coal and peat. Than the department of energy-chemical using of fuels was organized, which was headed by V.I. Tolubinsky. Experimental production workshops are being created.
By modern standards, the Institute was scarce: in 1950 it employed about 140 people (of which about 40 in the experimental-production sector), there were only 44 research staff. However, by the end of 1963, its staff was about 487 people, in particular including 125 researchers, 4 of them were doctors and 35 were candidates of sciences. In addition, about 80 employees worked in experimental production workshops. The Institute has thoroughly strengthened its production base. In 1962, the construction of a laboratory building with an area of 4800 m2 was completed, and in 1963 – an experimental building with an area of 2000 m2; several large experimental stands were constructed.
In 1963 the Institute consisted the departments: heat transfer (head O.O. Kremnev, later he became Academician of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR), thermophysics of high-temperature machines (E.P. Dyban, later he became Academician of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR), dynamics of heat processes (V.I. Fedorov), mining thermotechnics (Academician of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR O.N. Shcherban), analytical researches (M.M. Nazarchuk), fuel processes and boiler plants (G.L. Babukha), methods of direct conversion of heat into electric power (G.M. Shchoholiev), thermogasdynamics (O.S. Shvets), general energy (F.T. Markovsky).
Today, the Institute of Engineering Thermophysics (IET) of the NAS of Ukraine (till 1964 it was the Institute of Heat and Power Energy of the Academy of Sciences of the UkrSSR) is the leading Ukrainian center for heat and mass transfer, heat and energy technology and energy saving technologies.
In different years, the Institute’s scientific staff was headed by famous scientists: Academician of the Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR I.T. Shvets, Professor G.M. Shchogolev, Academician of the Academy of Sciences of UkrSSR V.I. Tolubinsky, Professor G.L. Babukha, Corr. member of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine O.A. Gerashchenko. Academician of NAS of Ukraine A.A. Dolinsky (now he is Honorary Head of the Institute) managed the work of the Institute from 1982 to 2015.
Since December, 2015, the Institute is headed by Yuriy Fedorovich Snezhkin, Academician of the NAS of Ukraine, Doctor of Engineering Sciences, professor, laureate of the State Prize of the USSR in the field of science and technology and laureate of the State Prize of Ukraine in the field of science and technology.

The main building of IET of NAS of Ukraine, 2a, Zhelyabov Str., Kyiv
In the structure of the Institute there are 12 scientific departments, research and design technological bureau on intensification of heat and mass transfer processes, experimental manufacturing, engineering center “Dry” and experimental mechanical plant of heat and mass exchange machines. On the basis of the Institute, by the Law of Ukraine, it was created the Technological Park “Institute of Engineering Thermophysics of the NAS of Ukraine”, whose president is Academician of the NAS of Ukraine A.A. Dolinsky.
At present, the Institute has about 400 employees, of which are 2 Academicians of the NAS of Ukraine, 7 Corresponding Members NAS of Ukraine, 23 doctors and 89 candidates of sciences. Over the years the Institute has formed a number of scientific schools and directions, which played the most important role in the field of heat power engineering and energy saving heat engineering. The founders of the most famous scientific schools are Academicians I.T. Shvets, A.N. Shcherban, V.I. Tolubinsky, A.O. Kremnov, A.A. Dolinsky, E.P. Dyban, Corr. Academy of Sciences of Ukraine O.A. Gerashchenko,
Many works of the Institute’s scientists were highly appreciated, they were marked by two State Prizes of the USSR, twelve State Prizes of Ukraine, three international awards by named O.V. Lykov, two prizes of the Presidents of the Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, Belarus, Moldova, five prizes by named G.F. Proskura of the NAS of Ukraine, four prizes by named V.I. Tolubinsky. More than 110 developments of the Institute have been awarded with diplomas and medals of domestic and foreign exhibitions. The high level of the Institute’s works are confirmed by 1,800 Ukrainian and foreign copyright certificates and patents for inventions.

Anatoliy Andreevich Dolinsky
Academician of NAS of Ukraine, Doctor of Engineering, Professor
Honored Worker of Science and Technology of Ukraine,
three times the laureate of the State Prize of Ukraine in the field of science and technology,
Honorary Head of the Institute of Engineering Thermophysics of the NAS of Ukraine
Since 1979 the Institute publishes the scientific and applied journal “Industrial Heat Engineering”, which since 1996 has gained international status. The English version of the journal has long been published in the US publishing house “Begell hоuse, Inc., Publishers”. The main results of the Institute’s scientists’ works are reflected in 120 monographs, published in various thematic collections, articles of the leading Ukrainian and international journals.
On the basis of Institute is functioned following: the National Committee for Heat and Mass Transfer, the CIS Committee on Drying Problems, the Section “Energy Saving and Environment in the Fuel and Energy Complex” of the Scientific and Technical Council of the Ministry of Fuel and Energy of Ukraine, the Scientific Council on the Problem “Heat Technology”. At the initiative of the Institute was founded the National Association of heat pumps in Ukraine (Public Union) in the beginning of 2015. This was done to popularize using heat pumps and promotion of the implementation of that technology in Ukraine. The Institute actively participates in the development and implementation of state scientific and technical programs.
The Institute has of two specialized Doctor and PhD Scientific councils for the defense of dissertations. The Institute’s staff has defended than 42 doctoral and 198 candidate’s dissertations.
The IET of NAS of Ukraine has constantly exhibition of the Institute’s developments “Energy and Resource Saving”. Experts of various branches of economy, students and teachers of universities and technical schools, responsible employees of ministries and departments, deputies of the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine, foreign guests and delegations introduce with the exposition.
The Institute’s specialists are members and experts of committees and scientific and technical councils at ministries, departments and state administrations on issues of production, transportation and consumption of energy.
The Institute pays considerable attention to innovation activity. It is a regular participant and organizer of international scientific and practical conferences and roundtables, specialized exhibitions. Together with the Chamber of Commerce and Industry of Ukraine, the Institute is searching for new promising forms of work with the attraction of investments for the effective introduction into the production of high-tech developments.
Exhibition hall of IET of NAS of Ukraine
on the 2a Bulakhovsky Str., Kyiv
The Institute give the propositions to the ministries to implement joint innovation projects with difference institutes of the NAS of Ukraine and production enterprises, initiates the creation and transfer of new technical objects and technologies for the production of competitive products in Ukraine.
The Institute’s staff is productively working on the implementation of state scientific and technical programs on the priority areas of science and technology development, creatively solves individual problems in accordance with the edicts of the President of Ukraine, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine and the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine.
The Institute gives much attention to the preparation of future changes. There are students of technical universities, and the best of them are still working at the Institute. Young scientists have the opportunity to participate in international scientific conferences. More than 50 young scientists are encouraged by the Institute’s special awards and targeted scholarships by named of famous scientist – founders of scientific schools, which awarded for creative achievements and successful scientific work on the development of new fundamental directions of the Institute replica rolex datejust.
The main directions of the scientific and technical activity of the Institute are:
- Thermophysical research of processes in heat and power equipment by using traditional and renewable energy sources and development of methods for increasing its efficiency, reliability and environmental safety.
- Development of heat exchange theory and its application for increase of efficiency of processes of transfer and use of heat in cars and devices of new technics.
- Development of the theory of heat-mass transfer for increasing the efficiency of existing and developing fundamentally new energy-saving and resource-saving heat technologies.
- Development of the measurements’ theory of thermal characteristics and its application in development of new thermophysical instruments and systems for increasing metrological maintenance of the exploitation of energy power and other heat engineering equipment.
According to the main directions of scientific and technical activity, the Institute’s scientists carry out research works on:
- development of the thermophysical processes’ theory in the objects of industrial and municipal energy, systematic analysis of strategic options for modernization of these industries;
- development of scientific bases and methods for increasing the efficiency of fuel use in power generation by combined heat and electrical power generation in heat supply systems;
- development of the general theory of turbulent heat transfer in complicated conditions, typical for heat power equipment, creation of scientific bases and methods of heat protection of high-temperature sets;
- research of the mechanism and regularities of the transfer process with changes in the aggregate state of heat carriers in the elements of the power equipment;
- thermophysical research of working processes in the equipment of nuclear power engineering, development of methods for increasing its reliability and environmental safety, methods for predicting thermogasdynamic events in the burial of radioactive waste from nuclear power plants;
- development of theoretical bases of heat and mass transfer in the conditions of discrete-pulse input of energy into dispersed environments and creation of a fundamentally new class of technologies on this basis;
- research of fundamental problems of non-stationary of heat and mass transfer in capillary-porous and colloidal bodies and rheological systems in the presence of phase and chemical transformations;
- research of the bases of heat and mass transfer’s intensification and development of effective heat technologies in the chemical, food processing and microbiological industry and construction materials industry;
- research of heat and mass transfer processes in case changing of aggregate state of a substance, creation of absorption refrigeration sets operating in refrigerator and heat pump modes;
- creation of devices and measuring systems for monitoring the composition of waste gases in power equipment, chemical and mechanical crash and optimizing the combustion process in furnaces of energy and heating units;
- creation of high-precision measuring devices and systems for carrying out of heat measurements in objects of municipal power engineering;
- creation of efficient gas cleaning systems and heat recovery devices.
The innovative approach has conditioned follow estimate of the marketing strategy of the Institute: based on fundamental research are developed new technologies and equipment, that are marketable and promising for the production of profitable products.
One of the main scientific directions that have been actively developing at the Institute over the last three decades is the research of methods for controlling heat and mass transfer processes and the creation of new energy-saving technologies on their basis.
Founders and leaders of this area of work are academicians O.O. Kremnev and A.A. Dolyńsky. The works of scientists Yu.F. Snezhhkin, V.R. Borovsky, J.M. Pievsky, A.V. Shurchkov, Yu.S. Kravchenko, L.M. Grabov were great contributors to the formation and research development.
To the highly effective and, almost, universal method of controlling the processes of heat and mass transfer in heterogeneous systems should include the method of discrete-pulsed energy input (DIVE), that was developed at the Institute under the direction of the academician of NAS of Ukraine A.A Dolinsky. The essence of this method is the accumulation in the working volume of the apparatus with a heterogeneous environment of heat or potential mechanical energy and its instantaneous transformation into kinetic impulses in time and discrete in space. The energy is brought directly to the border of the phase separation with the vapor (gas) bubbles, in the vicinity of each of them, as a result of growth, collapse or oscillation are initiated shock waves, cumulative jets, interphase turbulence, cavitation. Energy-saving property of this method is achieved by high level of specific power, local nature of the process and due to this sharp reduction of losses from energy dissipation in the entire volume of the device.
Experimental and theoretical researchs indicate that for a short time interval (of about 10 ns) the vapor inside temperature and in the vicinity of the extremely closed bubble changes to tens of thousands of degrees, and the vapor pressure in the bubble increases from 0.1 to 6000 MPa. The diameter of the bubble thus decreases from 1 mm to 100 … 200 nm, that is tens of thousands of times. Thus, processes of energy transformation in the implementation of methods of discrete-pulse input of energy are carried out in spatial and temporal nano-scales.
On the basis of the DIVE principle, the Institute developed dozens of innovative technologies related to grinding and homogenization of heterogeneous environments and the intensification of mass transfer processes in such environments, created fundamentally new classes of devices for such technological operations. In these devices, in comparison with traditional analogue equipment, differ significantly in their low energy intensity, various mechanisms of DIVE are used effectively, which are related to the dynamic effect of bubble structures.
Using of new technology 38 energy-saving, environmentally friendly technologies have been created. They have been successfully implemented in such industries as energy, metallurgy, construction materials production, cable industry, oil and gas industry, food, dairy, sugar, processing and canning industries, medicine, manufacture of pharmaceuticals, textile, leather industry, production of chemical fibers, etc.
In total, based on the practical implementation of the principle of DIVE have been developed more than 50 samples of equipment, 17 complex technological lines. The total number of installations implemented in the production exceeds 1000 units, which provides significant savings in fuel, raw materials, and metal.
Only in this scientific direction were obtained 76 patents and author’s certificates (A.A. Dolinsky, Yu.O. Shurchkova, V.O. Kremnev, O.A. Korchinsky, A.P. Gartwig, J.S. Kravchenko, B.I. Basok, O.F. Nemchin, O.I. Chayka).
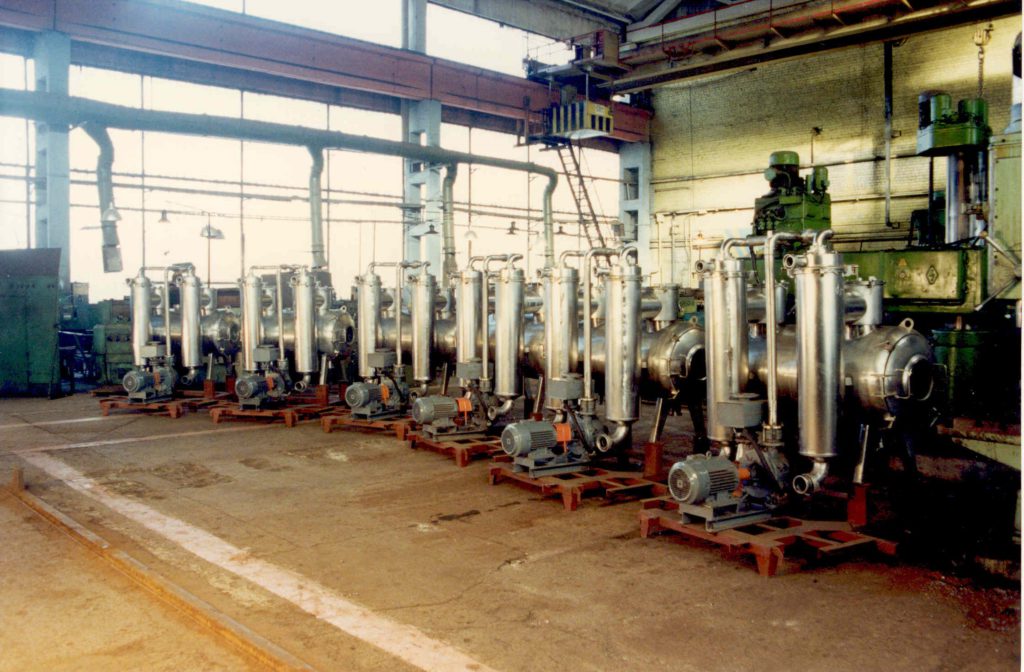

A party of vacuum homogenizers, that was manufactured by the Bolshevik plant,
prepared for shipment to food industry enterprises
The idea of this method was also used in developing the technology of obtaining a liquid milk substitute, introduced in 600 farms of Ukraine and CIS countries and awarded in 1984 by the State Award of Ukraine (A.A. Dolinsky, Yu.O. Shurchkova, Yu.D. Nikolaev and etc.).
In 1997, the author’s staff of the Institute was awarded the State Prize of Ukraine in the field of science and technology for the work “Creation and implementation of energy and resource-saving technologies and equipment on the basis of the principle of discrete-pulsed energy input”.
During 2004-2006 in the framework of the national program “Children of Ukraine” with the participation of the Institute of Pediatrics, Obstetrics and Gynecology of the Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, the IET of NAS of Ukraine, for the first time in Ukraine, developed hypoallergenic foods for infants and young children – “Dry mixtures adapted to hydrolysed protein for children’s medical nutrition”. On the basis of the results of studies of heat and mass transfer processes using the method of discrete-pulsed energy input was created a modern domestic energy and resource-saving technology of their production (N.O. Sharkova, L.Yu. Avedeva, Y.T. Terletska, E.K. Zhukotsky, G.V. Gryshchenko). Industrial testing of new technology, conducted at the Khorolsky dairy canning plant of children’s products, has yielded positive results. The cost of medical products manufactured using the new technology is approximately 1.5-2 times lower than the cost of imported analogues. During these works were received seven patents, five applications for the invention were filed, the results were widely presented at many specialized international scientific conferences, seminars, were covered in the mass media.
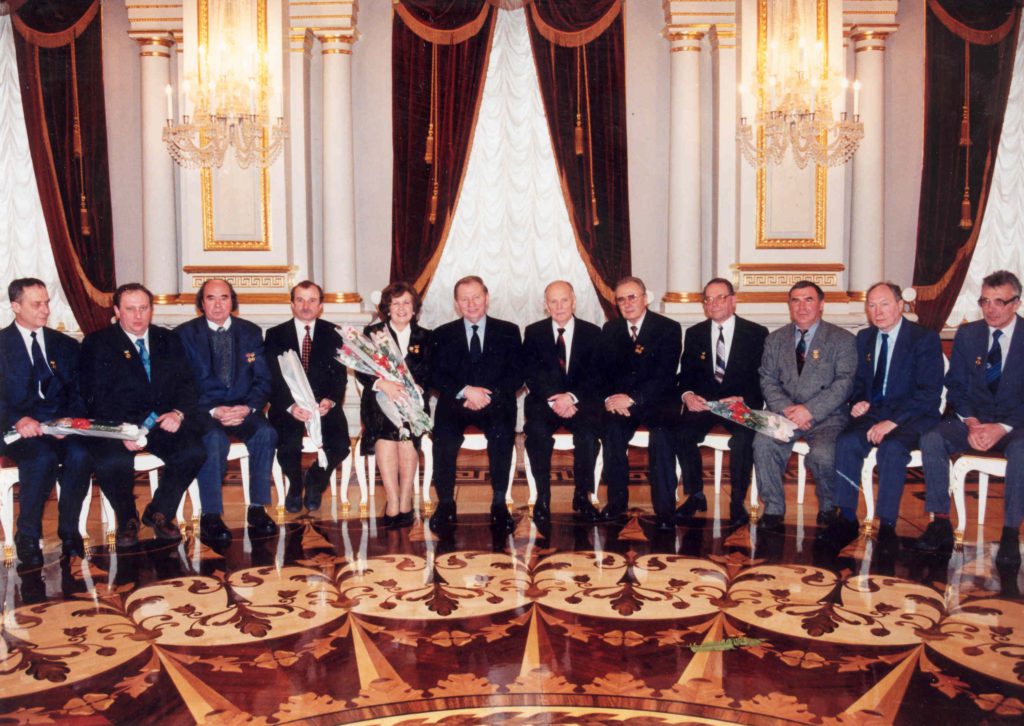

During the awarding of the State Prize of Ukraine in the field of science and technology
an author’s staff in the Mariinsky Palace in 1997, Kyiv
In 2005, A.A. Dolinsky was awarded with the International Prize by named Academician A.V. Lykov of the NAS of Belarus for the development of new theoretical and experimental methods for the study of heat and mass transfer processes and their using in industrial technologies. In the same year the Institute of Engineering Thermophysics of the NAS of Ukraine was awarded with the medal of the VI International Forum “High Technologies of the XXI Century” for the development of “Using the DIVE method in industry”.
As you know, 8% of all consumed organic fuel in the world is spent on drying processes. The Institute, with its research in the field of the theory and technology of drying, is one of the leading places in the CIS and is well known in the world.
Fundamental and applied scientific results cover the following areas: the theory of interconnected of heat and mass transfer processes, diffusion, filtration, evaporation and deformation in the dehydration of colloidal solutions and compositions, capillary-porous materials, methods for modeling the dynamics and kinetics of heat and mass transfer processes, optimization of heat engineering processes of drying.
They are developed theoretical bases of the interconnected heat and mass transfer processes, filtration, phase transformations and deformation in heterogeneous porous systems with one-and multi-component liquid phase, effective methods of computer modeling of dynamics and kinetics of drying, ways of improvement of the corresponding technologies.
A molecular-radiation theory of heat and mass transfer was constructed; equations were obtained for the intensity of evaporation and diffusion of a liquid in pores of a wet body, for capillary pressure in the liquid phase, depending on the structural parameters of the pore material and the degree of their filling with liquid.
On the basis of the conservation laws and the main provisions of the mechanics of a deformed body the general equation of the transfer of a substance (energy, mass, momentum) for a deformed body was obtained, which, in the absence of deformations, passes into the known Umov’s equation. At first time equations for the intensity of evaporation and heat of the phase transition of the components of the liquid mixture, the equations for equilibrium partial pressure of a vapor of the liquid’s components phase, from which follows the empirical laws of Raul and Henry (Corresponding Member Yu.F. Snezhkin, doctor of engineering M.I. Nikitenko), were obtained.
The concept and methodological principles of analytical and experimental research of heat wet transfer processes in complex interconnected aerodynamic and temperature-logistic conditions in chambers of spray driers and concentrators are developed.
There are developed new methods for controlling kinetic characteristics that are based on studies considering the system «drop (lobe) – vapor-gas environment as an elemental system in a complex aerodynamic environment of sprays chambers.
The results of fundamental research are scientific basis for improving the processes of spraying dehydration, intensification and optimization of heat engineering parameters, creation of new energy saving technologies and highly effective equipment for concentration and drying of specific groups of materials, taking into account the established thermophysical features of heat wet transfer in a separate dewatering drop (lobes).
Experimental and numerical studies of high-temperature dehydration of drops of different solutions for the first time convincingly showed the decisive role of internal processes of heat and mass transfer during spray-drying solutions. The idea of evaporative-drying dehydration of solutions in one unit was implemented in a series of apparatuses (ISA-7, ISA-200, ISAR-500, ISAR-7, etc.) and introduced into the medical, food and chemical industries (more than 100 units) in the former USSR and in other countries. This allowed to reduce energy consumption by two to three times for drying and improve the quality of products. The special resolution of the Central Committee of the CPSU on the basis of the ISA-200 unit in the country created the industry of dry blood substitutes (polyglyukin L-103, etc.) (A.A. Dolinsky, A.T. Malushenko, A.P. Gartwig, C.D. Maletska, L.M. Maslyugov).
At the Institute the method of high-temperature drying of materials by a high-humid heat carrying and steam-depressant drying method were developed. It was used in the creation and implementation of high-intensity drying installations in the building materials industry, in the production of food products, fabrics, in the drying of silk cocoons, viscose silk and a number of other materials (O.O. Kremnev, V.R. Borovsky, V.O. Shelimanov, J.M. Pyevsky, E.S. Malkin).
Technology and equipment for non-waste processing of apple puddings and the obtaining of food products from them have been developed. In 1984, the this work was awarded the State Prize of the USSR (O.O. Kremnev, V.R. Borovsky, Yu.F. Snezhkin, L.M. Grabov). Seven sizes of technological lines have been created and implemented.
Handshake during the start of the evaporative and drying unit, India, 1996
In Vietnam common with Ukraine, two processing plants for tropical fruit powders are organized. Contracts for manufacturing technological equipment for Slovakia have been concluded. The Ministry of Health of Ukraine has developed and approved normative and technical documentation for powders of apples and their pans, table beets, carrots, pumpkin, cabbage, squash and beet pulp. More than 100 names of food products containing powders containing medical and prophylactic properties have been developed (Yu.F. Snezhkin, L.M. Grabov, V.R. Borovsky, G.K. Vospitannikov, A.O. Khavin). In 2006 a cycle of works on the creation of powder compositions of health nutrition was awarded to the State Prize of Ukraine in the field of science and technology (Yu.F. Snezhkin, K.D. Maletska)
A new resource-saving technology for producing low-methacylated pectin from apple powder has been developed. The preparation has a significantly higher activity and ability to bind heavy metal ions, in particular a number of radionuclides, than the usual pectin. Comparing with known methods, the process of obtaining an active form of preparations is accelerated several times. The technology was introduced in Ukraine at the Bar Tanner Plant, in 1995 the production of pectin from local raw materials was established in India (B.M. Protsyshyn, R.S. Weinberg, S.A. Bogdanov, M.D. Butsky).
The study of the disintegration of a stream in a drop under the conditions of external harmonic oscillations made it possible for the first time in world practice to develop a new type of dispersion device. It provides monodisperse drops systems for grinding liquids, to create industrial designs of vibration granulation equipment for installations of monodisperse granulation of products, to develop an engineering method of their calculation. Systems of monodisperse granulation of nitrogen fertilizers are widely implemented at the enterprises of the branch. In the 80’s a complex of works was made to create monodisperse product granulation systems. This work in 1983 was awarded the State Prize of the Ukrainian SSR in the field of science and technology. In recent years, based on this method, it has been created a technological line for the production of simulated caviar. The line has been implemented at four enterprises in Ukraine. One line is delivered to Spain (Yu.S. Kravchenko, B.V. Davydenko, A.I. Teslya, L.O. Vasilchenko).
At 72 plants of the former USSR a significant reduction in energy consumption and improvement of the quality of gypsum products was given by a new drying technology which is based on the using vapor depressive method with a zonal change in the dewatering regime (J.M. Pyevsky, R.O. Chernyshova, G.D. Nazarenko).
The proposal theory of the transfer of soluble macromolecular substances from the external solution to the capillary-porous colloidal body and the study of the kinetics of fixation of dyes on textile materials under thermal and thermoelectric fixation methods have enabled a group of scientists (V.R. Borovsky, E.S. Malkin, L.M. Grabov) to develop a number of energy-saving technologies for the textile industry:
- technology of fixing dyes on textile materials after printing in overheated steam (3.5 – 6 times increased productivity of existing equipment, 2-4.5 times reduction of specific energy costs); 110 installations were introduced;
- technology of high-speed convection-radiation fixation of dyes on textile materials at air temperatures exceeding the temperature of destruction of the material (the time of fixation of dyes has been reduced by 10-20 times, the specific energy costs are reduced by four times).
In the Institute technology of high-speed drying of mulberry cocoons was developed using the vapor. This technology was adopted for the technical re-equipment of the entire industry in the former USSR, mass production of equipment was organized and more than 1,100 installations were implemented. Their application made it possible to accelerate the drying process three to four times and increase the yield of raw silk by 0.5-1.5% (V.R. Borovsky, L.M. Grabov, M.D. Korostash).
Since 1975, under the leadership of B.M. Protsyshyn there are carrying out works of intensify the processes of drying in the technology of microbiological manufactures, to obtain dry forms of microbiological preparations intended for the control of pests of agricultural plants (as an alternative to chemical preparations), on the research of heat and mass transfer processes in biosynthesis and dehydration of microbial biomass on the basis of entomopathogenic fungi. It formed the basis of technology and equipment for obtaining ready-made forms (fine particles or granules) of spore mushroom preparations by the combination of deep and solid phase fermentation. This technology and equipment have no analogues in the world of practice (B.M. Protsyshyn, S.V. Beregov, V.V. Mikhalevich, V.A. Tarasovets).
In the Institute, based on new, more efficient processes of hydrodynamic grinding, homogenization and extraction of multicomponent environment using non-standard heat and mass exchange equipment have been developed a number of new technologies for obtaining powder products and new preparations for children’s and health nutrition.
More than 30 years ago, the academicians O.N. Scherbanem and O.O. Kremniev proposed a fundamentally new technology for extracting heat from the earth’s interior by creating systems with the forced circulation of coolant. The doctor engineering sciences A.V. Shurchkov created a unique laboratory model of the geothermal circulation system, developed methods for calculation and optimization of geothermal power plants. The first geothermal station was built in 1983 in the village Ilyinka (Crimea), which works now (A.A. Dolinsky, A.V. Shurchkov, G.M. Zabarny, etc.).
With the connection huge prospects for the production of geothermal energy in Ukraine and the current energy saving policy, the need for sorption thermotransformers will increase in the coming years. In the Institute, as a result of many years of research have been developed industrial thermotransformers from 10 to 3000 kW, which makes it possible to increase the energy efficiency of the heat-carrier (geothermal water) by 70%. Such transformers are successfully implemented today, including abroad, for the use of solar energy (O.O. Kremnev, V.Ya. Zhuravlenko, E.R. Grosman, B.C. Shavrin).
The scientific direction of the school, which was founded by academicians I.T. Shvets and E.P. Dyban, is the research of the heat-physical processes taking place in the heat-and-power equipment in order to create effective systems of its heat protection.
At the Institute, such research was carried out on gas turbine engines and plants, internal combustion engines. The scientific basis of these works was a complex of theoretical and experimental researches of heat exchange in conditions that are characteristic of such objects – in the action fields of large mass forces, in highly turbulized and pulsed flows, in jet streams, and others like that.
As a result of many years of joint work with Design Offices of leading power machine-building enterprises were elaborated methods for cooling parts of gas turbines and methods of their engineering calculation, which was summarized in the monograph by E.P Diban and I.T. Shvets “Air-cooling of gas turbine parts” and in the three-volume “Guidance notes”. These materials became the main manual for designing air-cooled systems. At the same time, under the guidance of M.V. Stradomsky there were developed methods for cooling the components of internal combustion engines (ICEs).
Under the leadership of I.T. Shvets and V.Y. Fedorov theoretical and experimental researches of non-stationary processes in steam and gas turbines were carried out, the method of calculation of transient processes of turbo-compressor aggregates was developed including the gradual calculation of turbines, taking into account the accumulation of heat by the apparatus of the blade. The obtained results are used for the development of control systems for gas turbine units GTU-50-800, GT-16-750, K-500-240 turbine units, etc. at the Sverdlovsk and Kaluga turbine factories, the Nevsky plant, the Leningrad metallurgical plant and the Kharkiv turbine plant.
Under the leadership of Corresponding Member NAS of Ukraine A.A. Khalatov (later becoming academician) a significant cycle of research on heat and mass transfer and hydrodynamics of single-phase and two-phase flows in the fields of centrifugal mass forces was carried out. At the first time the conditions for the similarity of internal twisted streams and their stability were formulated, new methods for calculating swirling flows in channels that surpass those existing in accuracy were created (A.A Khalatov, A.A. Avramenko, I.V. Shevchuk).
On the basis of carrying out fundamental research new scientific results, which substantially deepened and expanded the modern notions about the physical structure of the flows, the mechanism of turbulent heat and mass transfer in the field of centrifugal mass forces of different nature were obtained. This made it possible at first time to substantiate the conditions of physical similarity, to develop new models of turbulent transfer, to create improved methods of analysis of centrifugal instability, to offer more precise methods of calculation, to develop the scientific foundations of new vortex technologies. In particular, at first time are discovered and investigated new physical phenomena – “compression” of the vortex and accumulation of energy in it, “suppression” of turbulence by rotating stream, the coexistence of regions of active and conservative action of centrifugal mass forces in a twisted flow, and the formation of a universal profile of speed.
The fundamental multi-volume monograph “Heat transfer and hydrodynamics in the fields of centrifugal mass forces”, which six volumes came out of printing in 1996 – 2006, in fullness and scientific novelty of the materials presented in it exceeds modern editions in this field.
Fundamental works are closely linked to applied research in the field of power engineering, heat engineering and heat and power engineering. Among the most important practical results should be included methods and programs for calculating vortex and twisted streams, which are widely used by design organizations of heat and power engineering. For power machine building new technologies of oscillating film cooling, vortex technologies of flow separation control and secondary currents in turbomachines have been developed. At first time the innovative technology of internal cyclone cooling of turbomachine blades, which was developed in IET, was used in practice by firms in the United States and the United Kingdom. Currently it is accepted for use at the Zorya-Mashproekt (Ukraine) plant for the creation of powerful energy gas turbines.

Handing by NATO Secretary General Lord J. Robertson
the first international prize of the NATO Scientific Committee, Brussels, 2002
(the second from the left – Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine A.A. Khalatov).
A significant cycle of applied defense works in aerospace and aviation technics has been completed. It was supported by seven decisions of policy makers. Recommendations for cooling high-temperature nozzle devices with intensive vortex structures were used for modernization of the cooling system of the gas turbine of the SU-27 combat aircraft and its modifications. For Design Office “Yuzhnoye” (Ukraine) the conditions for thermostabilization of instrumentation compartments of missile systems were substantiated, for the Rocket Center by named V.P. Makeev (Russia) the works on the program of the strategic system of “Typhoon” submarine navy were completed. For Design Office by named P.O. Sukhoi (Russia) the vortex principle of reducing the “thermal sensitivity” of high-temperature outgoing jets of power plants of aircraft was developed.
For fundamental and applied researches the Institute’s staff awarded two scientific awards of the NAS of Ukraine by named outstanding scientists (Corresponding Member of the NAS of Ukraine A.A. Khalatov, candidate of engineering I.I. Borisov, the doctor of engineering N.V. Kostenko), the first international prize of the Scientific Committee of NATO (Corresponding Member of the NAS of Ukraine A.A. Khalatov). For merits in the development of aerospace engineering, Corresponding Member NAS of Ukraine A.A. Khalatov awarded with the RosAviakosmos’ medal “40 years of Y.A. Gagarin’s flight into space”. In 2010 Corresponding Member NAS of Ukraine A.A. Khalatov in the composition of the author’s collective awarded the State Prize in the field of science and technology.
The IET of NAS of Ukraine successfully develops a scientific direction related to solving the inverse heat transfer problems. In such problems, according to the measurement of temperatures in certain points, boundary conditions on the surface of bodies were sought, for example are the heat fluxes on the shell of descending spacecraft, thermophysical characteristics of the thermal protection of the same apparatuses, the magnitudes of heat dissipation in the device elements, and others.
Before the beginning of the 1990s, at the Institute there were three departments of the theoretical profile related to the simulation of heat and mass transfer processes – under the leadership of the doctor of engineering Professor L.O. Kozdoby, doctor of engineering Professor M.I. Nikitenko and candidate of engineering O.O. Grechany. In these departments, methods were predominantly developed and practical solutions to direct and inverse heat transfer problems were performed. The most interesting solvable inverse problems include the determination of heat transfer conditions on heat-loaded surfaces of blades and assemblies of gas turbine engines and heat exchangers, determination of thermophysical characteristics of heat-shielding materials in the operating conditions of their heating, determination of thermal flows and thermal state of products under jet cooling and boiling, and others like that. Five monographs and a significant number of articles were published at the Institute on the subject of inverse tasks.
At present, in the Institute there is department of modeling of heat and mass transfer processes, which is headed by doctor of engineering Professor P.G. Krucovsky. In this department on the basis of new methods and computer technologies, practical direct and inverse problems of heat and mass transfer in the most general formulation are solved. The so-called calculation-experimental approach to the modeling of heat and mass production processes and the optimization of product parameters is actively developing, in which the solution of inverse problems is an important link not only to identify the coefficients of these models, but also to ensure the adequacy of the models used in order to further solve optimization and forecasting tasks.
The most interesting and important for the practice solving the reversed tasks include the development of models and the solution of the tasks of estimating average operating temperatures and predicting the resource of protective coatings of gas turbine blades (a project supported by the NATO scientific program) and the problems of prediction of thermal deformations and precision forging when turning parts (work with Magdeburg University, Germany). In these jobs reversed tasks are an important part of ensuring the adequacy of the models used to predict.
Three-dimensional CFD-models have been developed and calculations for checking the efficiency of the project of the ventilation system of the Arch of the New Safe Confidential over the object of the Chernobyl NPP shelter have been made on the basis of the analysis of the Arctic thermal state under given conditions of operation of the ventilation system. The results of the work allowed to provide suggestions on a new scheme of the ventilation system of the Arc. The Institute did the work by winning the international tender (P.G. Krukovsky).
The idea of direct conversion of heat into electricity is very attractive and relevant. In different countries of the world well-known scientists worked on the implementation of the idea of MHD generator. Works in this direction at the Institute were carrying out by G.M. Shchogolev, E.T. Baseev, V.G. Nosach, and S.V. Dubovsky. The method of thermal protection of the walls of the MHD channel by injecting gas through penetrating walls has been used to create gas-permeable hollow cathodes for a current up to 10,000 A for plasma sets, a unique plasma melting furnace and crystallization of especially refractory materials (above 4000 K). So, an oven for produce CaTi was created, which is using in industry instead of technical diamonds (Yu.P. Kukota). These works are implemented in industry, albeit on a limited scale.
Among the important research carrying out in the Institute, which were not sufficiently widely implemented for a number of reasons, includes the work on the energy technology using of Ukrainian brown coal, which was carried out in 1949-1957 in accordance with the decision of the Council of Ministers of the UkrSSR. As a result of these works (under the leadership of V.I. Tolubinsky and G.M. Shchogolev) were developed all possible variants of using: direct burning, gasification and semi-coking at combines for receiving electric power, products of chemical processing of resins, including the receipt of artificial liquid and gas fuel. On the basis of these works, a re-equipment for such an Alexandrian CHP plant was started, which was mothballed due to the development of huge oil and gas fields in Siberia and their transportation to the European part of the USSR (V.I. Tolubinsky, G.M. Shchogolev, M.I. Rabinovich, N.M. Pyatishkin, V.I. Kovaliv, A.N. Kocherezhko, G.L. Babukha). It is possible that the current situation in the fuel and energy complex of Ukraine will make the problem of brown coal use up-to-date.
Among the perspective problems belong V.G. Nosach’s proposal to increase the coefficient of efficiency of heat technical units by thermochemical regeneration. Calculations show that with the help of thermochemical regeneration, the efficiency can be increased for DNB by 7 – 12%, for GTU – by 5 – 10%, for CHP – by 4 – 15%, for industrial furnaces – by 20 – 30%.
Carrying out experimental research with Kansk-Achinsk and Ekibastuz coal, anthracite loam, sunflower husks, and sawdust showed that high-speed heating (heat stroke) in hot products of combustion allows practically instantaneous transfer of a large part of the organic mass of coal into the gas phase. As a result of such thermochemical processing fuel consisting of a pyrogas and a fused cooker residue is formed. The burning of this fuel in the furnace showed that it is practically free of undigested and is distinguished by its high ecological purity. This technology was introduced at the Poltava oil extraction plant for sunflower husk combustion and Olkhovetsky sugar plant for the burning of low-grade fuel oil.
The Institute is one of the leading organizations in the field of heat transfer research in changing the aggregate state of matter and using the results of these studies for improving the equipment of steam turbine and nuclear power plants.
The founder of the works in this field is Academician V.I. Tolubinsky. Under his leadership a series of works on boiling physics and the theory of heat exchange during boiling was carrying out. Extensive research of the mechanism of the process was carried out, as a result in the most complete and reliable data on its internal characteristics for a variety of pure liquids, binary mixtures and solutions on the surfaces of heating from various materials in a wide range of pressure were givin.
A considerable cycle of works on thermophysics of water cooling nuclear reactors has been carried out, numerous experimental work on boiling crises in pipes, ring channels and rod beams of various configurations with uniform and uneven heating in a wide range of defining parameters and geometric sizes has been performed. The obtained ratios included in the “Guiding technical materials” from the heat-and-hydraulic calculation of heat-exchange equipment of the NPP (V.I. Tolubinsky, E.D. Domashov).
The methods of intensifying the heat transfer during boiling in channels, increasing the critical density of the heat flow and correspondingly increasing the capacity of the nuclear reactor have been developed. The optimal modes and designs of the intensifying devices are determined, the calculated relations for determining the possible increase of the critical density of the heat flow and the output vapor content are developed.
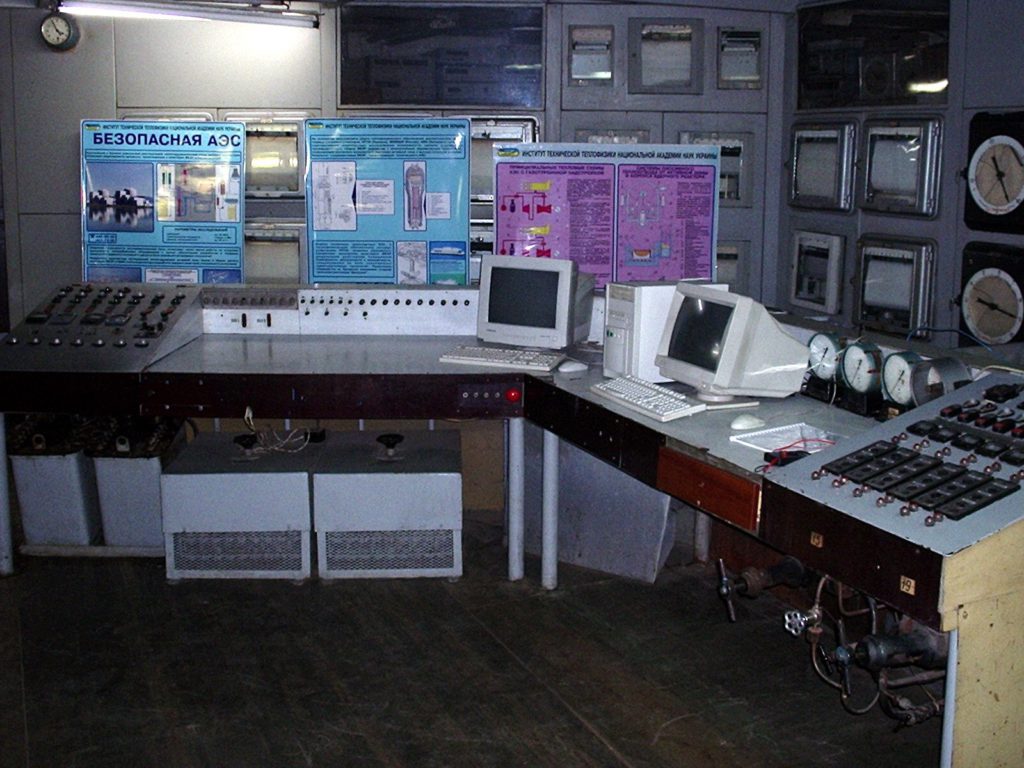

Thermophysical stand “Ring” of high parameters: pressure up to 20 MPa, density of heat flow up to 8 MW/m2.
At the stand the experiments on the heat exchange crisis in pipes, ring channels and beams of rods of different configurations with different form and uneven heating (common 3 thousand points) were made.
The specialized means of measuring the thermophysical parameters of the NPPs were developed and investigated, in particular automatically high-speed measuring instruments and the propagation of sensors signals system of intra-reactor thermal control (V.I. Tolubinsky, E.D. Domashov, V.F. Godunov, M.M. Kovetska). It is proposed the acoustic registration method of the boiling beginning, the emergence of a boiling crisis (A.M. Kichigin, A.A. Moskalenko).
At first time in the country they were developed high-temperature coaxial heat pipes with radial heat transfer and high stability of temperature support in the range 800-1.300 K. On this basis, together with a number of the ministries’ organizations of the former USSR, the industrial plants for the production of semiconductor devices and growing of single crystals were created (E.M. Shevchuk).
In the Institute the complex of works on the development of effective profiles of heat transfer surfaces was carried out simultaneously in two directions: the research of the heat transfer of finite surfaces with a change in the shape of perforation, roughness and size of ribs in a wide range of ranges and the creation of high-performance equipment for pipe bending (jointly the Institute of Electric Welding by named E.O. Paton.). This made it possible to develop and implement in the energy sector a large number of high-performance heat exchangers for various purposes: steam separators, superheaters, heaters, heat exchangers for the utilization of the heat of exhaust gases, waste heat boilers, etc. (V.I. Tolubinsky, N.V. Kukushka, V.V. Treputnyov).
One of the important scientific directions of the Institute is the mining thermal physics. Works in this area began under the leadership of O.N. Scherban. The theory of non-stationary heat and mass transfer and hydrodynamics in porous layers and rock massifs has been developed, the thermophysical and mass-exchange characteristics of capillary-porous bodies have been experimentally studied, methods of gas-dynamical phenomena pro-gnosis during coal mining, in particular, the sudden emission of gas, have been developed. The complex problems of non-stationary heat exchange between air of mines and an endless rock mass are solved, and methods of calculating the temperature of air in dead ends are developed, where air is fed by a special air duct.
Applied works connect with the creation of new and improved existing air conditioning systems and the management of the thermal factor by the ventilation regime of deep mines, subways and other underground structures, the development of equipment for the study of temperatures, thermophysical and mass transfer characteristics of rocks.
Based on these works, powerful installations for air conditioning of deep mines of the Donbas and a number of other mines, have been developed air conditioning systems projects for unique underground structures have been created.
The complex of works in this area was awarded the State Prize of the USSR (1969, O.N. Scherban, O.O. Kremnev, V.P. Chernyak). Under the leadership of Academician O.N. Scherban ways of extraction of mercury from ore in underground conditions by a thermal way, a method of diamond production and other equally exotic technologies was developed. That needs industrial inspection and refinement in future.
Relatively recently the Institute has begun working on the problem of burial’s radioactive waste, which is topically for Ukraine today.
Already the scientific basis for the long-term forecasting of the thermal regime of underground workings and the surrounding massif of rocks at the buries of the radioactive waste of energy and industry in geological formations and their isolation has been developed. The methods of thermal calculations and the principal schemes for the removal of excess heat from storage facilities have been developed. The results of these works are used in Ukraine in substantiating the choice of geological formations for the burial’s radioactive waste, the thermophysical maintenance of a safe and environmentally safe storage facility (V.P. Chernyak, A.S. Polubinsky, and E.M. Malashenko).
In 1971, the Institute began working on a new scientific direction – thermometry. Founder and leader was Corresponding Member of NAS of Ukraine O.A. Gerashchenko.
On the basis of these works the theory of signal generation in thermometric transformers of heat flow of various constructions has been developed. On the basis of theoretical positions and experimental methods of constructing transformers with the necessary metrological characteristics and technology of their production data are offered.
An original base flow sensor was developed. On its basis were made more than 100 modifications of the derivatives of specialized devices for the determination of thermal conductivity, heat loss, radiation characteristics, calorimeters, ionizing radiation dosimeters, actinometers, pyrometers, etc. They have been widely used in energy, nuclear physics, medical and technical diagnostics.
For non-destructive heat control of materials and products they developed heat-measuring flaw detectors for operational control of the quality of thermal insulation, heat-shielding properties of building structures – heat loss and thermal flow meters of the ITP series.
Another scientific direction in the field of instrument making is the development of scientific bases of tools for automatic control of the content of combustible gases and vapor in the atmosphere and the quality of combustion of gaseous, liquid and pulverized fuel in industrial units. Works in this direction were initiated by Academician O.N. Scherban. They became the basis for the creation of the first domestic thermocatalytic devices IM-2 and IM-3 for automatic control of methane in the atmosphere of coal mines. More than 1,500 sets of these devices have been implemented in gas-hazardous mines of Donbass and Kuzbas. The devices were marked by a bronze medal at the Brussels International Exhibition in 1958.
The Institute made a significant contribution to the creation of a large nomenclature of thermophysical instruments. In connection with solving a large number of technological problems and problems of energy saving especially acute the operational control and regulation of heat transfer processes and minimization of heat losses by various objects, mainly energy and construction industry have become.
The achievements of thermometry, electronics and metrology of the heat flow measurements allowed to develop a range of modern metrologically certified devices and computerized complexes for measuring heat flux, temperature and thermophysical characteristics in order to minimize heat losses at all stages: from heat production to heat-generating enterprises and its transmission through heat conductors before using it by various consumers.
Measuring instruments that promote the efficiency and optimization of heat production processes include the developed in IET of NAS of Ukraine: bomber conductive calorimeters of the KTS models for the determination of fuel quality; a group of devices for controlling combustion processes in terms of the number of unburnt substances in the delivered ash and in flue gases of boiler units (devices for controlling the mechanical and chemical inclining of fuel); radiometers RAPP-5, RAP-12 for monitoring the irradiation of heat-stressed areas of the flue space of boilers of communal and industrial power; indicators of thermal losses of ITP-13, ITP-20 and others for the operational control of heat losses due to lining and heat-insulating protective structures of boiler units; the computerized universal measuring complex “Resource” for the determination of damages of pipelines and steam pipes, fences and thermal insulation fences; computerized systems of IMRT-1 and “Trassa” for the determination of temperature fluctuations on elongated sections of underground main heating mains and actual integral thermal losses during operation without disconnection of the customer, etc.
During 50 years of thermometry development have been created more than 200 types and models of primary transformers and thermophysical devices on their basis. Together they have been introduced about 20 thousand primary transformers, devices, sets, installations and information-measuring complexes on various enterprises, in particular the heat and power sector. Complex of performed works in the field of heat energy became part of the work of the IET of NAS of Ukraine, which awarded with the State Prize of Ukraine in the field of science and technology in 2005.
The problem of the country’s energy security, reducing the consumption of energy resources put new tasks front of scientists. Now physicists are actively working on the development of concepts for a significant reduction of energy consumption by the municipal services complex, regional concepts for modernizing energy resources of regions.
In the condition of rising energy prices and increased environmental safety requirements, the efficiency of using energy resource depends a lot on the use of advanced energy-saving technologies, which enables using more efficient of energy resources and increased environmental safety of energy supply.
One of the ways solving these problems is creating and implements new heat engineering processes using efficient energy saving equipment – heat pumps. Heat pumps can realize the transfer of low-temperature heat, which is unsuitable for direct use, to a higher temperature level and can be used for receiving hot water for heating, hot water supply and other purposes. The almost inexhaustible source of energy for heat pumps is the heat of industrial secondary energy resources, domestic wastewater, the environment (air, water pool, ground).
The Institute accumulated more than 40 years of experience in the research and creation of heat pump pumps sorption and compression types. Different modifications of sorption thermotransformers for industrial technological processes and for systems of heat supply of municipal objects have been developed. At first time in the USSR two-stage bromystolytic thermotransformer with a cooling capacity of 3.0 MW was created and introduced in the production plant at Penzhkimmash. An efficient technical solution was used in the unit – an energy-saving working cycle with a step-by-step regeneration of the solution, which reduces the consumption of primary thermal energy by 1.6 times and reduces the cooling water consumption by thermotransformer by about 40%.
With the participation of the Institute’s specialists about 30 absorption transformers were commissioned at the enterprises of chemical, rubber, and metallurgical industries, in particular at the Kyiv Volcano Plant, Chelyabinsk Cotton and Magnitogorsk Metallurgical Combine. For a number of enterprises, in order to achieve the maximum effect from the use of absorption transformers original technical solutions for the inclusion of absorption and refrigeration machines (ABCMs) into production schemes have been developed, which protected by patents.
Thermotransformer with the capacity of 3 MW, which was implemented
in mass production at Penzkhimmash Plant, Penza, Russia
The Institute carries out research on the creation of sorption cooling and heat pump plants for municipal facilities that works with the using renewable energy sources, in particular solar energy. It has been completed a large amount of theoretical and experimental research on the looking for new working bodies for these systems.
Various modifications of the condensation type heat pump units, which were developed in the IET of NAS of Ukraine, have been implemented in the Republic of Vietnam, a number of Ukrainian enterprises, in particular heat pumps, dry heaters, thermoplastic heat pumps, drying heat pump units for the polyethylene terephthalate processing line, etc.
The Institute developed energy-saving schemes of heat supply of municipal objects based on heat pumps using heat of wastewater, ventilation emissions, heat of secondary energy resources.
An important direction in reducing the energy consumption of municipal and industrial heat power engineering is the widespread using cogeneration heat technologies (simultaneous production of thermal and electric energy). The main scientific tasks of the Institute in this direction are the development and improvement of methods of thermodynamic analysis for optimization of heat circuits and the choice of heat-mechanical equipment of cogeneration units, optimization of waste heat utilization in heat circuits with gas-piston and gas turbine engines, on the basis of which the development of cogeneration units is carried out, and practical creation and introduction of these technologies in municipal and industrial heat power engineering.
Work in this direction was carrying out in 1996-2002 under the leadership of Correspondent member of NAS of Ukraine V.M. Klymenko. In 2005 the department of combined energy technologies was created, that supports and develops the works on cogeneration. The head of the department is doctor of engineering B.D. Bileka. Similar works are carrying out in the department of small energy under the leadership of Correspondent member of NAS of Ukraine N.M. Fialko, and in the department of thermophysical foundations of energy-saving technologies, headed by Correspondent member of NAS of Ukraine B.I. Basok.
The Institute developed and implemented a number of cogeneration units based on gas turbine units (GTUs) and gas-piston engines (GPAs). Thus, in particular, the first cogeneration units based on a 2.5 MW gas turbine engine was developed and introduced into experimental and industrial operation, and the exhaust gases are discharged into the boiler, at the municipal boiler of Zaporizhzhya. On the basis of the GPA three cogeneration units in Simferopol (Fiolent plant) with a capacity of 1 MW at the industrial enterprises, and in Gostomel and Kostopol, at glassworks with a capacity of 0.5 MW were developed and put into operation.
For gas turbine systems the basic scientific provisions and practical proposals for new energy-saving anhydrous technologies with the use of low-boiling working bodies at utilization of waste heat of compressor stations of main gas pipelines in power and power-cooling plants have been developed. Together with OJSC “Sumy NGO by named M.V. Frunze” of a power-generating unit with a working body of n-pentane with a capacity of 4 MW was developed, manufactured and commissioned in the pilot-industrial operation.
With the direct participation of the Institute’s specialists developed and subsequently approved the Law of Ukraine “On combined development of electric and thermal energy (cogeneration)”.
For the needs of heating and hot water new, more advanced and economical boilers to replace the morally and physically obsolete boiler systems of municipal power engineering have been developed.
One of them is a water-heating water-tube boiler, that works under a pressure of natural gas of low pressure with a heat productivity of 2.0 MW (KVV-2.0 Gn). It was developed under the scientific guidance of V.T. Rogovoy. This boiler is intended for using in heat and hot water supply systems, it provides an increase of efficiency up to 95%, even when reducing the load. The boiler allows putting the return water with low temperature starting at 35 °C; it has a long and effective lifetime, is available and easy to repair, has a high efficiency of 93 – 94%, low nitrogen oxide emissions (up to 80 mg/m3). Serial production of boilers KVV-2.0 Gn was started on the basis of the leasing enterprise (OPE) “Krymteplocomunenergo” (Simferopol).
Under the leadership of O.I. Sigal and V.N. Kanygin a boiler with a water-tight water pipe-fired heat productivity of 0.63 MW (KVVD-0.63 GH) was developed, which uses the advantages of gas-pipe boilers (small metal and labor capacity) and water pipes (high efficiency of heat exchange). The combined KVVD-0.63 Gn with a heat productivity of 630 kW with forced circulation of the coolant through the boiler is calculated for works on natural gas or light liquid fuel and is intended to produce water with a temperature up to 95 0С and a pressure of up to 0.6 MPa for heating, technological needs and hot water supply. Implementation of boilers will allow replacing obsolete boilers of the type “Minsk-1”, “NIISTU-5”, “Universal”, “Energia”, etc., to increase the efficiency and reliability of heat supply sources.
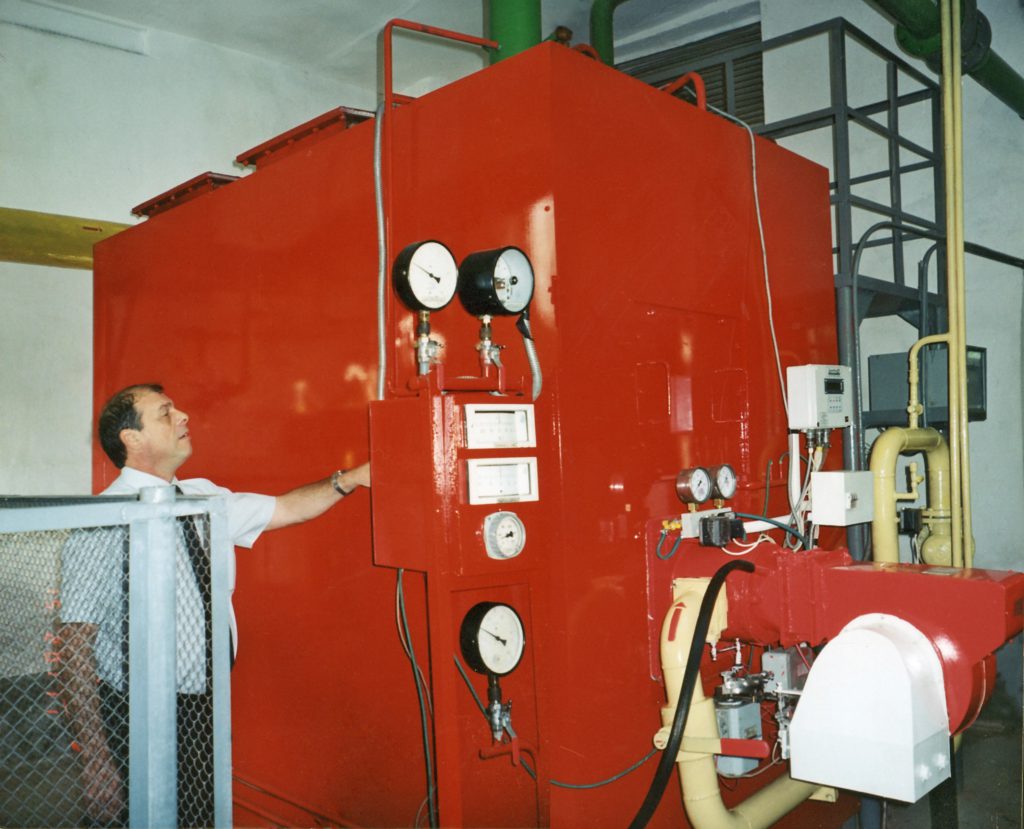

The head of the leased enterprise “Krymteplocomunenergo” I.V. Vail examines the boiler KVV-2.0 Gn,
Crimea, Simferopol
The results of the carrying out scientific researches show that the widespread use of a number of technical solutions and developments, which staff of IET of NAS of Ukraine is actively working on, can reduce fuel consumption in small energy and municipal services by 30% due to:
using of modern boiler units with a higher efficiency and boilers that work on local fuels (straw, wood, peat, etc.) for heat supply;
development and improvement of modern computer models and programs for the analysis of combustion processes in power units for to improve their designs and more efficient work;
the application of new, more sophisticated and less energy-expending schemes with heat pumps for the heat supply of buildings and enterprises;
using of solar energy with helping of seasonal accumulation and low-potential secondary heat of industrial enterprises;
widespread introduction of cogeneration cycles, that provide additional electricity generation at gas stations;
the deep utilization of the heat of the exhaust gases of the boiler plants by using the heat of condensation of water vapor and the more advanced heat exchange equipment;
improvement and mass implementation of modern devices complex of heat accounting and control, management and automation for heat and power equipment in power engineering, construction and industry;
using of individual heat points.
IET of NAS of Ukraine plays a prominent role in the development of regional programs for the modernization of municipal heat power engineering and on the basis of their national heat supply strategy. The goal is to reduce consumption of natural gas to 30% in the sphere of municipal services due to increase of energy efficiency of its using and replacement of other types of fuel.
There was conducted a systematic analysis of the current state of municipal heat power engineering in Ukraine with the definition of key problems, ways and measures for its modernization.
It was developed a complex of methodological, scientific and technical and organizational principles for radical improvement of territorial heat supply that has practically been worked out on a scale of industrially developing and ecologically and socially tense region. The further this experience can be using as a basis for the development and implementation of programs for other regions and on their basis, the State Target programs of modernization of municipal heat and power engineering of Ukraine.
There are developed a number of draft decisions, state regulatory acts, which define the scientific and technical ideology and policy on the development of municipal heat power engineering in Ukraine.
On the basis of the results of fundamental and applied researches in the branches of thermophysics and heat engineering new energy-efficient technologies have been created and equipment and their production has been adjusted.
The modernization of the municipal heat power engineering of the Donetsk region was made, where in 2010 the natural gas savings amounted to 80 million m3 (27.5%), 274 tons of nitrogen oxides and 146 thousand tons of greenhouse gases were reduced. Total natural gas savings since 2004 amounted to 348.5 million m3 (for current subsidies for heat municipal services – 363 million UAH). The pilot project of the regional program paid off for 4 years and became a base for 17 regions.
According to the developed methodology, that was approved by international expert organizations, a number of Joint implementation projects under the Kyoto Protocol mechanisms have been established, whereby Ukraine’s heat supply companies received 260 million hrn. irreversible investments, including Donetsk region – 76,4 mln. (Academician of NAS of Ukraine A.A. Dolyinsky, A.M. Bliznyuk, Corresponding Member of the NAS of Ukraine B.I. Basok, Corresponding Member of the NAS of Ukraine Yu.F. Snezhkin, Corresponding Member of the NAS of Ukraine Н.M. Fialko, A.I. Segal, G.P. Kuchin, E.T. Baseev, A.I. Chayka, D.Yu. Paderno, V.A. Vorotintsev, V.M. Kucherenko, J.Ye. Khivrich).
In 2013, Corresponding member of NAS of Ukraine Natalia Mikhailovna Fialko as a member of the scientific team received the state award of Ukraine in the field of science and technology for the work “Energy-efficient technologies of accelerated construction of industrial and civil engineering objects”. In this work the scientific and technical bases and were introduced a complex of energy-efficient technologies of accelerated construction of industrial and civil engineering objects, advanced heating technologies of buildings and corresponding construction norms were developed. The scientific substantiation of a number of new and improving technologies of accelerated industrial construction has been fulfilled: the application of high quality coatings and the construction of seamless floors and platforms, strengthening of grounds by using of enzyme preparations, including received on the basis of nanotechnology, etc. A new high-performance composite material using of new generation of basalt fiber has been created. The main provisions of the energy saving technology of heat accumulation floor electric heating have been developed. For the conditions of accelerating panel construction of housing, the scientific basis for creating energy-saving enclosure constructions of buildings has been developed. Approaches to solving complex problems of building thermophysics on the basis of the theory of localization are developed. The methodology of construction of the domestic normative base for energy efficiency of buildings is developed.
In 2014, Corresponding member of the NAS of Ukraine Andriy A. Avramenko, as a member of the scientific team, received the state award of Ukraine in the field of science and technology for the work “Creation and implementation of competitive socially oriented textile and leather materials and products with predictable technical and medical and biological properties”. In this work the system of prediction of properties of textile materials in the dynamic conditions of their production is developed. This makes the possible to get textile materials with given properties. An important socio-economic plan is the development of domestic types of special protective clothing for firefighters, for employees of nuclear power plants, personnel protection against X-rays, clothing for miners (clothes are exploited at the Shelter (ChNPP) facility). At first time in Ukraine technological clothing for high-tech enterprises with so-called “clean rooms” (chemical and pharmaceutical enterprises, production of precise mechanics, securities and documents with special means of protection, production of electronic equipment, etc.) was developed.
Recently, have been initiated a number of studies for energy engineering.
IET of NAS of Ukraine continues to plan fundamental research on thermophysical processes in order to acquire new knowledge for the improvement of heat and power equipment, development of energy saving technologies for energy, industry and agrarian complex.
The Institute aims to find and implement new forms of work with the regions of the country, innovation funds and banks to attract investments in the development and implementation of the latest energy-efficient technologies.
Its future Institution relates the best graduates of universities to the scientific work, improves the state of the material and technical base, and increases the level of international cooperation, first of all when carrying out joint projects with scientists from the countries of the European Union, Russia, the USA and other countries.